Biology News and Articles
Declining House sparrows (Passer domesticus): Is our ecosystem healthy enough to support all forms of life ?
House sparrow is a small perching bird (Passerine bird), which has feet that are adapted for perching. Though it is native to Europe, Asia, and Mediterranean region, it also spreads to north and south America and some parts of Africa. So, it is one of the widely distributed and well adapted bird to live along with humans in urban cities. Among the members of the family Passeridae, Indian house sparrow is the least migrant bird. It is closely associated with human beings and his domesticated animals. Hence, it has got its species name “domesticus”. These sparrows perch on the weed stalks for collecting seeds and perch on the tree barks for finding out insects for its young ones. This is a monogamous (mono: single; gamous: marriage or mating) bird, which has a single mate at any one point of time.
Life span
The life span of this bird is around 13 years. However, its annual survival rate is 45-65%.. After leaving the care of their parents, young sparrows have a high mortality rate, which lessens as they grow older and more experienced.
Only about 20–25% of birds that are hatched, survive to their first breeding season. These cute little birds are disappearing from us and it has been felt in several western European countries too. Before we proceed to discuss about this issue let us learn about some basic terminologies being used in ecology, a branch of biology.
Community
In ecology, the word “community” refers to the assembly of populations of two or more DIFFERENT SPECIES exist in the same geographical area. So, all the living organisms including plants, animals, microbes are a part of our community.
Ecosystem
An ecosystem refers to the community of living organisms of a particular geographical area along with its non-living things. Obviously the non-living things of a particular area include the natural resources of our planet earth such as soil, water, air and so on. This non-living thing of a particular area is known as habitat.
An ecosystem can be as small as an area under the rock or as big as an ocean. When we talk about the surrounding environment in which an organism lives, we use the term “habitat” . In an ecosystem all the living organisms depend on each other for survival.
So, there exist a complex set of relationships among the components of an ecosystem including plants, animals, birds, trees, fishes, water, soil, air and people. Each of the living and non-living components of an ecosystem are a functional unit of that ecosystem. If any of these parts are destroyed or disappeared it has an impact on everything else.
Let us consider the factors that may be responsible for the decline of this small
birds. They are,
i) Modern agricultural practices : use of insecticide and land use change
House sparrows depend on insects for breeding and seeds for survival. Agricultural intensification, lack of field borders in farming land (In Europe, even a small bit of land won't be wasted in the cultivation area), use of crop seeds that are more competitive than the local weeds, use of pesticide and urbanization have put the survival and breeding of this small bird in jeopardy.
Non-availability of soft bodied insect larvae as food for the young hatchlings of house sparrow is an another reason that is attributed to its decline. It is said that the newly hatched young ones eat only these insect larvae,which are disappearing due to the use of insecticide in the farmland and home
garden.
The concept of ecology can clearly be understood in this process, where the man's selfish interference with the components of an ecosystem such as land, and insects affects the food chain of house sparrows. Now, the house sparrows are deprived of their food and are in danger.
ii) Non-ionized electromagnetic radiation from cell phone base station
A group of scientists from the research institute for Nature and Forest studied the effect of long term exposure of house sparrows to low-intensity electromagnetic radiation from mobile phone base stations in six different areas of Belgium. They found that the number and behavior of male sparrows were negatively affected by the radiation at different levels in different geographical
locations in Belgium. It was suggested that both the survival and reproductive capacity of the birds were negatively affected by this electromagnetic radiation emanating from this cell phone towers.
iii) Non availability of native trees and plants
Due to urbanization, there is no place left empty for the weeds and other local plants to grow. In the home garden people prefer to grow ornamental plants of foreign origin. We should know that our native birds and animals have adapted themselves to eat and rely on the plants originated from our region.
iv) Noise pollution
Due to noise pollution, birds may not be able to communicate with their young ones and mates by chirping in urban areas.
v) Use of unleaded petrol
The lead was earlier added to petrol to boost up its burning efficiency, but the lead was found to accumulate in children’s bodies and gradually damaging their brains. After a long struggle the unleaded petrol became available in 1988 in Europe. However, the compounds that replaced the lead were yet another hazardous chemicals: Methyl tertiary Butyl Ether (MTBE), and Benzene.
Both are toxic and hazardous to health and cause cancer in animals. Dr. Summer Smith, an engineering consultant and former scientific advisor to ICI (Imperial Chemical Industries) has been studying sparrows intensively for over 50 years. He pointed out that there is a strong connection between the introduction of unleaded petrol and the decline of house sparrows in United Kingdom. This is also evident from the fact that the house sparrow population was unaffected in France as compared to other European countries due to the use of diesel in cars. In France the price of diesel is cheaper than that of the petrol.
Conclusion
A sharp decline of house sparrows may be due to one or more of the factors that we discussed above. If we want to save this beautiful bird at first we must aware of the causes of its decline.
“To be humane is not only about showing kindness and compassion to fellow human beings but also to be kind to all the living organisms of our ecosystem”.
Please do remember that each and every living things on the earth has an equal right to live happily and peacefully like any other living creature. Let us respect and protect our fellow living creature.
How can you help this little bird?
-By growing native bushes in your home garden.
-By creating awareness among public about the causes of its decline.
- Check noise pollution at your home and in your garden to provide a conducive
environment for all sorts of birds.
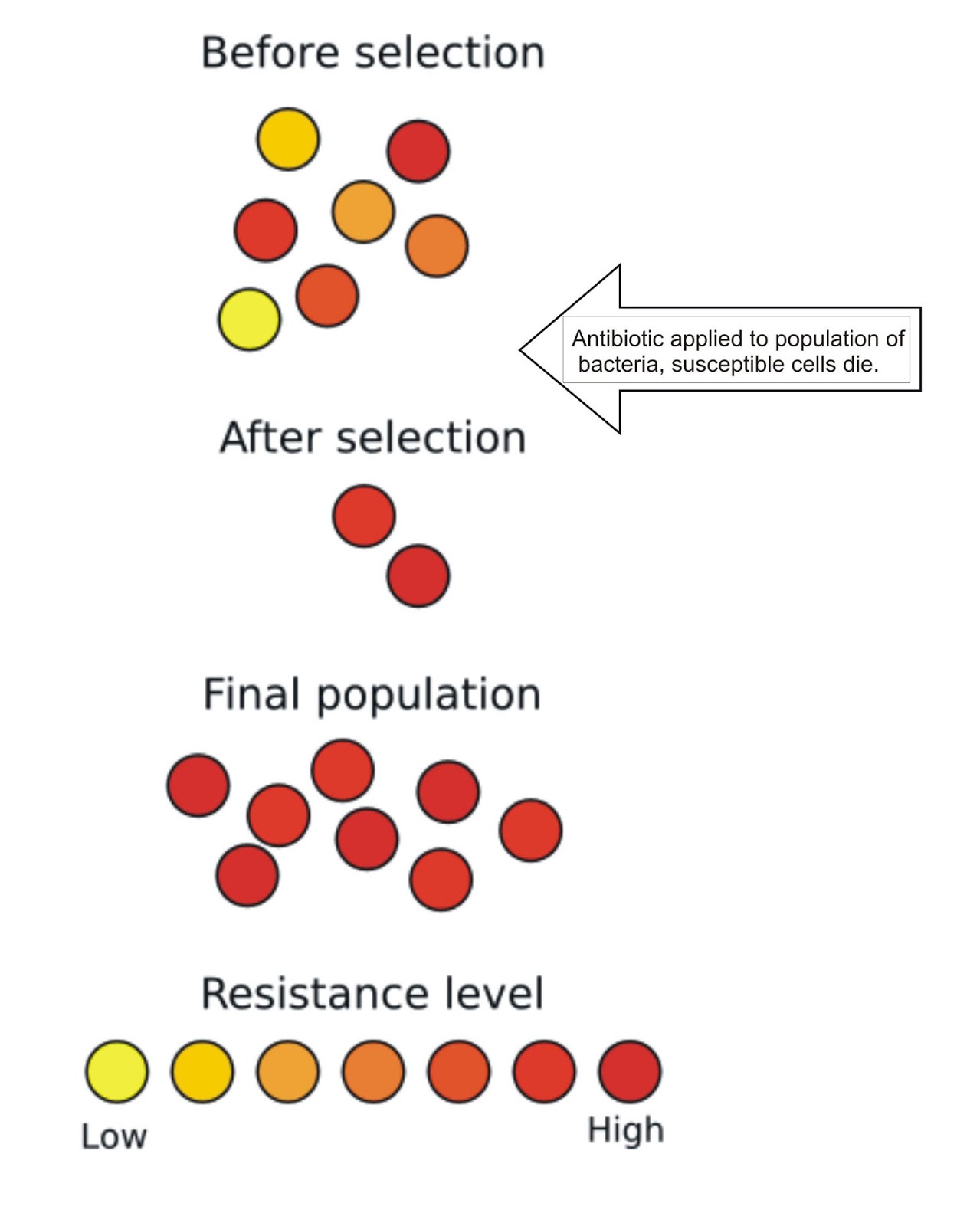
How do bacteria become antibiotic resistance?
Frequent and improper use of antibiotics promote the multiplication and spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria, while it selectively kills the sensitive bacteria.Antibiotics are the antimicrobial drug used to fight the infection caused by bacteria.
The first antibiotic
“penicillin” a natural antibacterial agent produced by fungus was discovered by
Alexander Fleming. So, this natural antibiotic has the ability to kill bacteria
that cause disease in both humans and animals. Not all antibiotics are natural
some may be synthetic which can either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria.The discovery of antibiotics has undoubtedly revolutionized the way of
treating the bacterial infections in humans and animals.
Thus the smart use of
antibiotics is the need of the hour to control the spread of antibiotic
resistant bacteria.





Comments
Post a Comment